Updated 2026-01-13
Top dbt Alternatives
🔧 Transformation Only
📦 Full ETL Suites
☁️ dbt Cloud Alternatives
What is dbt?
(If you are already familiar with dbt, skip to Considering Alternatives)
Data transformation is an integral part of the modern data stack, and dbt (data build tool) has emerged as a frontrunner in this space. This tool is unique in that it focuses exclusively on the ‘T’ in ELT (Extract, Load, Transform), setting it apart from traditional tools that encompass the entire end-to-end pipeline.
According to their own YouTube video, titled “What is dbt”, dbt Labs tells us they built dbt on two core beliefs:
 1 - Transformation logic (i.e. business logic) should be defined in code. This is SQL, jinja, YAML, and more recently Python. dbt is by all means a code-first platform, and seems like they have no intention of jumping on the low-code bandwagon.
1 - Transformation logic (i.e. business logic) should be defined in code. This is SQL, jinja, YAML, and more recently Python. dbt is by all means a code-first platform, and seems like they have no intention of jumping on the low-code bandwagon.
2 - Treat data assets like a product.
This second point has been a differentiator for dbt. It was the first to bring software engineering best practices to data pipelines. This includes version control via Git, automated testing of your data pipelines, and deployment via CI/CD. It also simplifies the workflow of working in environments (Dev, QA, Prod), and gives a very clear way to migrate through the environments.
But what IS dbt? dbt is a transformation tool that allows anyone comfortable with SQL to author their own data pipelines. When it comes down to it, dbt is just a clever way to organize and document your SQL files, visualize the data lineage via a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph), and execute very specific segments of the DAG or pipeline. Additionally, dbt is very tightly integrated with Git, so code is version controlled and has a defined release process. dbt encourages, but does not require use of CI/CD for deployment. dbt is compatible with almost any database, and offers jinja functions to ensure cross-database compatibility.
To dive deeper on the question “What is dbt”, I recommend this YouTube video by Seattle Data Guy. He does a great job of comparing the old workflow in SSIS to the new workflow in dbt, highlighting why dbt represents a paradigm shift.
dbt Core
The “Core” offering, called dbt Core, is an open source python library. You install it with pip, just like any python library, but that is where the Python ends. You can use dbt with zero Python knowledge; the Python is just responsible for executing SQL, displaying the documentation and other backend stuff.
dbt Core allows an analyst familiar with SQL to express complex transformations in the form of the SQL SELECT statement. Instead of writing DDL (create table) and DML (Insert, update, delete), the analyst will simply create the SELECT statement and dbt will handle the rest.
Table models will re-create an entire table from scratch every time. When you want to insert new rows, use an incremental model. If you need a slowly changing dimension, dbt has an out of the box solution for that called dbt Snapshot.
dbt Platform (formerly know as dbt Cloud)
dbt Platform is dbt’s commercial product. It is a fully managed environment which hosts dbt Core for you and provides these extra features:
- Scheduling and pipeline observability
- Documentation browsing (or now “dbt Mesh”)
- Cloud based IDE aptly named “dbt Cloud IDE”
- Git integration (GitHub, GitLab, etc.), with a simplified “Git with guardrails” workflow
- CI/CD Integrations
- A catalog feature called dbt Explorer. It’s actually quite good.
- API for calling jobs externally, or querying logs, etc.
dbt Fusion
dbt has always been known as the open source transformation tool, but now that is changing a little bit with a new offering called dbt Fusion.
dbt Fusion is a re-write of the dbt engine in Rust. We’re not going to get into it too deeply here, but you need to know the basics:
- It is free to use, just download the rust binary and you’re up and running
- It is a mix of closed source and “source available” code. The code is entirely maintained by dbt Labs (now Fivetran)
- dbt Fusion has an extension for Visual Studio Code (or Cursor, or any vs code fork) which offers some nice features such as instant feedback on your code, lineage, preview CTEs or models to name a few.
- It is currently in the early stages, so you may face some compatibility issues
- Just like dbt Core, Fusion can be run locally for free, or in dbt Platform, for Platform customers.
- Platform customers get a few extra benefits.
dbt Bottom Line
dbt has become more or less a standard in the data transformation space and is the only open source tool in the modern data stack to achieve this status. While the market for Extract / Load tools, Integration tools, and Orchestration tools is quite crowded, dbt is currently the king of code-based transformation.
Personally, dbt has completely transformed (pun intended) the way I work. I cannot imagine doing a data engineering project without dbt. It is a common reaction for people to hear about dbt and say “why do I need that?”. This was also my first reaction too! You have to use dbt to get the first-hand “wow factor”. The first time you build a big project with 100+ dependencies and tests, it is a thrilling experience to watch it run what it can in parallel and wait for certain objects to run in series. You realize how much power and ease they have given you.
Who owns dbt?
Recently dbt Labs was acquired by Fivetran, announced in October 2025. It is yet to be seen how this will change the direction of the product.
Considering Alternatives
If you are looking for an alternative, it is important to ask yourself if you are looking for an alternative to dbt Platform / Cloud (you want to use dbt but not their commercial product), or, if you are looking for a complete alternative that doesn’t use dbt under the hood. This article highlights both pure alternatives to dbt and alternative ways to run dbt outside of dbt Cloud.
Transformation Only dbt Alternatives
Do It Yourself
This is a typical design pattern for DIY transformations:
- Create stored procedures to manage transformations (insert, update, delete)
- Likely, the stored procedure will be fed by many SQL views, or the procedures themselves will create or replace tables along the way
- If you are very advanced, a migration tool such as “Flyway” can be used to manage the various environments and deploy the code to Production
- Schedule it somehow:
- Airflow or similar orchestrator
- Use serverless functions like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Run
- Cron jobs to schedule the procedures
- If you are using Snowflake, it is common to use Snowflake Tasks to schedule the stored procedures
Advantages to DIY
- Full control
- No vendor lock-in
Disadvantages to DIY
There are a few problems with this approach, many of which are the reason why dbt was invented.
- Documentation is decoupled from the transformation itself. Where is it anyway?
- It is hard to understand the data lineage
- It is hard to know if everything is running on schedule (depending on which scheduling approach you did)
- You’re probably not version controlling everything, unless you fall into that advanced category
- Going from Environment to Environment is a lot harder
- You are not likely to come up with a better solution than using a tool
While this is a valid approach and many teams are still doing this today, I would encourage you to find an alternative to this dbt alternative! (Perhaps consider using dbt? 🙂)
Coalesce: A direct “transformation only” competitor
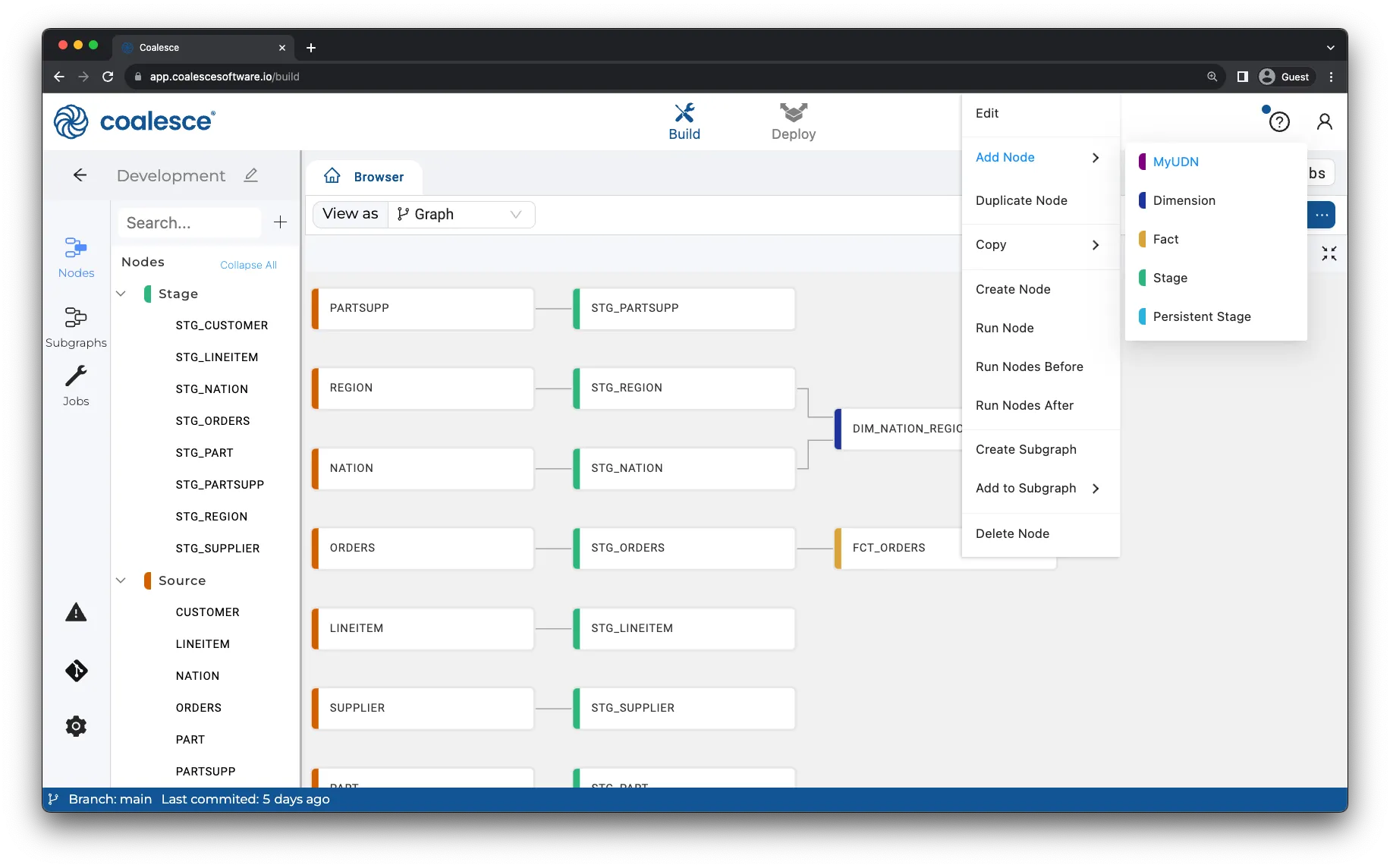
Coalesce (https://coalesce.io/) is a transformation platform that has evolved significantly since I first wrote about them. Originally built exclusively for Snowflake, they’ve now expanded to support Databricks, BigQuery, Redshift, and Microsoft Fabric. Like dbt, they focus exclusively on the transformation layer, but with a fundamentally different philosophy.
Coalesce is metadata-driven and GUI-focused rather than code-first, which completely changes the development experience. You can create all staging models for an entire schema with a few clicks, then layer in your custom business logic. The workflow continues with the same efficiency as you build facts, dimensions, and reporting models. They’ve struck an interesting balance between visual development and the flexibility of code—both technical developers and SQL-savvy analysts can be productive immediately.
Since I last covered Coalesce, they’ve added several features that push them closer to being a complete data platform rather than just a transformation tool. They now include a built-in scheduler (no more relying on external orchestrators or Snowflake Tasks), an AI copilot for code generation, and a data catalog for discovery and documentation.
Advantages and Key Features of Coalesce
Here’s what stands out to me in 2025:
- Column propagation: Automatically push new columns to all downstream models. If you’ve ever added a column to a source and manually updated 15 models, you’ll appreciate this
- JSON unnesting with no code: This alone saves hours on projects with semi-structured data. Yes, you can build dbt macros for this, but having it built-in is huge
- Metadata-driven development: Build transformations with a GUI that incorporates column-level metadata and context right where you need it
- AI copilot: Get code suggestions and accelerate troubleshooting with AI-assisted development
- Column-level lineage: See exactly how changes impact downstream models at the column and object level
- Built-in scheduler: No need for Airflow, Dagster, or Snowflake Tasks. Orchestration is now part of the platform
- Data catalog: Search, discover, and document data assets (tables, columns, dashboards) across projects
- Native warehouse features: GUI support for Snowflake Dynamic Tables, Streams, Databricks features, BigQuery equivalents, etc. They’re not abstracting away platform capabilities—they’re making them easier to use
- Marketplace packages: Standardized logic templates to enforce architectural patterns and speed up builds
- Environment management: GUI-based dev/test/prod configuration with proper documentation
- Preserve time travel: Table models use truncate + insert instead of drop/create, keeping Snowflake time travel accessible
Disadvantages of Coalesce
Here’s where Coalesce still has room to grow:
- Integration ecosystem: Fewer native integrations compared to some full ETL platforms. You’ll likely need complementary tools for ingestion
- Community maturity: The community isn’t as developed as dbt’s open-source ecosystem. With rapid adoption and multi-platform support, this should improve
- Platform-specific features: Some advanced capabilities are more mature on Snowflake than on Databricks, Fabric, Redshift, or BigQuery. This is changing as their platform support deepens
- Vendor lock-in considerations: It’s not open source, and while you can export the generated SQL, migrating away would require effort. (Though to be fair, avoiding vendor lock-in usually means rolling your own solution, which I rarely recommend)
Coalesce Quick Comparison to dbt
- Platform support: Coalesce supports the major cloud data warehouses (Snowflake, Databricks, BigQuery, Redshift, Fabric). dbt supports these plus many more databases
- Development approach: Coalesce is metadata-driven with a GUI + SQL hybrid. dbt is code-first
- Speed of development: Coalesce’s visual approach with AI copilot and marketplace templates can significantly accelerate development, especially for repetitive patterns
- Built-in features: Coalesce includes scheduler, catalog, and column-level lineage out of the box. dbt requires dbt Cloud or external tools for scheduling and has column-level lineage in dbt Explorer
- Code flexibility: Both give you full SQL control when you need it, but Coalesce also lets you work visually when that’s faster
Coalesce Wrap Up
It’s hard to capture the full power of Coalesce in a blog post (same issue with dbt—you really need hands-on experience). What sets Coalesce apart is how the metadata-driven approach, visual development, and automation features combine to make transformation faster and more governed without sacrificing flexibility.
If you’re evaluating transformation platforms, especially if you’re on Snowflake, Databricks, or the other major cloud warehouses, Coalesce deserves serious consideration. The time savings on repetitive work alone can justify the investment.
My advice: request a demo and see it in action. The difference between reading about it and watching it work is substantial.
Sign up for a demo here: https://coalesce.io/request-demo/
SQLMesh
SQLMesh, also acquired by Fivetran in 2025, is a true alternative to dbt Core. Like dbt Core, it is an open source python framework that helps you manage execution of SQL files in DAG order. But that is almost where the similarities end.
It is backwards compatible with dbt, meaning you can bring your own dbt project and run SQLMesh. But when coding from the ground up, we operate a little differently. We don’t use {{source}} and {{ref}}: One key differentiator of SQLMesh is that it can inspect your SQL to figure out your DAG without needing source and ref macros.
Another key differentiator is the idea of Virtual Data Environments, which ensures a table is never built more than once. Instead of each developer creating their own dev environment (such as dbt_jeffskoldberg schema), SQLMesh’s environment management system will know to use prod upstream sources when editing a SQL file. When you promote your changes from dev to prod, there is no need to build the prod table. SQLMesh will automatically point to the asset you built during development.
Advantages of SQLMesh:
- No need for YML files, but they are supported
- In-line documentation in the SQL file, instead of separate docs
- No need for
source/refmacros. Everything is simplified - They have built a beautiful UI which is an IDE and DAG viewer
- The UI has Column Level Lineage
Disadvantages of SQLMesh:
- There is a bit of a learning curve. The environment management is just different enough that it will take a day or two to switch from dbt. But certainly anyone who can learn dbt can learn SQLMesh
SDF - Acquired by dbt Labs in January 2025
Since SDF was acquired by dbt Labs, it is no longer a product that is available, and therefore not a dbt Alternative. However, I think it is valuable to keep this section for historical purposes. Many people don’t know what SDF was or how its roots shapes the dbt Fusion product today.
What was SDF?
SDF, which stands for Semantic Data Fabric, was another true dbt Core alternative as it sat squarely in the Transformation step of ELT. It played a very similar role to dbt, acting as a way to organize and orchestrate your SQL files in DAG order. It also had a built-in database engine powered by Apache DataFusion.
SDF was FAST
SDF had a few key differentiators. First, speed. It was written in Rust which meant it was blazing fast. Before using SDF I was never bothered by the compilation time of any dbt command. But after using SDF, a simple dbt compile felt soooo slow. Everything about SDF was so fast it almost seemed impossible.
Multi-Dialect SQL Compiler
The next differentiator was they had written their own multi-dialect SQL compiler (as opposed to a SQL parser). SQL parsers have the potential to parse queries that won’t actual compile or execute in the database, or miss nuanced changes in data types that can break downstream models. Quoting sdf.com, SDF “understands proprietary dialects of SQL (like Snowflake) so deeply that it can ultimately execute them.”
Built-in Database Engine / Emulation
This meant you could execute warehouse code locally. I thought of it as similar to duckDB, but it was actually powered by Apache DataFusion. The key advantage was that you didn’t need to run all of your code in the data warehouse. You could process some of initial models locally, materializing the final analytics tables in the warehouse. This seemed pretty groundbreaking - as it gave opportunity to reduce cloud compute.
This feature was in Alpha stage for Trino at the time of the acquisition.
Advantages of SDF
- The built-in SQL compiler eliminated the need for
sourceandrefmacros. It also guaranteed your code would execute properly - You could statically verify (in seconds) if a model change broke anything downstream, without executing anything in the data warehouse
- Local execution of data models (Alpha)
- Shipped with Dagster; no need for separate infrastructure if you already ran Dagster
Disadvantages of SDF
- Required WSL on Windows
- Not open source
Many SDF Features are now in dbt Fusion
Since SDF was acquired by dbt Labs, many of these features, including the multi-dialect SQL Compiler, have been built into dbt Fusion. Hopefully one day source and ref will go away and we can get something that looks more like SDF config. (SDF also had killer data governance features for tracking column masking policies. Please dbt!)
Data Platform Native SQL Orchestration
Major cloud data warehouses offer built-in SQL orchestration capabilities that can serve as lightweight alternatives to dbt for simple transformation workflows. These are pure SQL solutions - no additional frameworks, no Python, just SQL queries with scheduling built into your data platform.
Snowflake Tasks is the most mature option, offering SQL-based DAG orchestration with dependency management. You can create task trees that execute stored procedures or SQL statements in a defined order, with retry logic and monitoring built in. Snowflake also offers Streams for change data capture and Dynamic Tables for declarative, auto-refreshing transformations.
BigQuery Scheduled Queries (GCP) allows time-based scheduling of any SQL query with parameterization for incremental loads. Queries can be scheduled via the console or API, with results automatically written to destination tables. However, there’s no native dependency management - each query runs independently.
Databricks Delta Live Tables provides a declarative SQL framework for building data pipelines with automatic dependency detection and data quality checks. While transformations are SQL-based, pipeline configuration requires UI or JSON definition.
Redshift Query Scheduler (AWS) offers basic query scheduling but is quite limited - primarily useful for administrative tasks rather than complex transformation pipelines.
CI/CD and Production Considerations
These platform-native tools generally lack Git integration and require homegrown CI/CD pipelines. Most teams use Terraform or platform APIs to version control and deploy these SQL orchestrations across environments. Snowflake Tasks comes closest to production-ready with better error handling and observability, while BigQuery and Redshift require more manual infrastructure for proper deployment workflows.
When to Use Platform-Native SQL Orchestration
These tools work well for:
- Simple, scheduled transformations without complex dependencies
- Teams heavily invested in a single cloud platform who want minimal additional tooling
- Proof-of-concept projects before adopting a full transformation framework
However, they lack dbt’s testing framework, documentation generation, and cross-database portability. For anything beyond basic scheduled SQL, most teams adopt dbt (with dbt Cloud or external orchestration) for the richer feature set.
Transformation only tools - bottom line
With both dbt and SQLMesh now under the Fivetran umbrella as of 2025, the competitive dynamics have fundamentally shifted. SQLMesh, which once appeared to be dbt’s strongest competitor, is no longer a true competitor since they are owned by the same parent company. This positions Coalesce as dbt’s primary competitor in the transformation-only space. While SQLMesh remains a technical alternative worth discussing, from a business standpoint, Coalesce is the one I see going head-to-head with dbt.
Full ETL Suites
Moving on from “Transformation Only” tools, we need to look at tools that offer data movement + transformations.
Informatica
Informatica is a long-standing dynasty in the ETL space. They are extremely popular with Fortune 500 companies due to their monolithic nature; it is a single platform that handles all aspects of data integration, transformation, data quality, data governance, and API management.
Informatica has two main products in the ETL space, Informatica Power Center and Informatica Intelligent Cloud Services (IICS). While there are important differences between the two products, for the sake of this discussion, suffice it to say that Power Center is the traditional, self hosted version and IICS is the cloud PaaS version of the product. IICS offers additional features focused on cloud integration, but overall the two products are quite similar.
IICS Quick Comparison to dbt
- If you want to do in-database transformations as dbt does, IICS sells connectors separately for each database. You can pay a handsome fee for a Snowflake or Big Query connector (pricing is consumption based, hard to estimate)
- IICS is capable of doing in-memory transformations, in the more traditional ETL approach
- The data lineage will not be as clear to non-technical users compared to dbt
- IICS is very expensive. The pricing is not transparent, but is on the high end of the spectrum. You also pay for additional connectors; a Snowflake connector may cost an extra $25,000
Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) is a versatile ETL tool from Microsoft that serves as an alternative to dbt. Unlike dbt, which focuses on in-warehouse transformations using SQL, SSIS provides a comprehensive suite of tools for data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL). It excels in handling complex data integration workflows and offers a rich set of built-in tasks and transformations. SSIS is particularly strong in scenarios involving diverse data sources, including SQL Server, Oracle, and file-based sources. It’s a great option for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. However, SSIS’s user interface and deployment process can be more complex compared to the simplicity of dbt’s code-centric approach.
SSIS Quick Comparison to dbt:
- More than just a transformation tool
- Historically transformations are done before loading (in memory of the SSIS server), although options exist to do in-database transforms
- Data Lineage will not be as clear to a non-technical user
- Documentation will be held outside of the platform
Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is a cloud-based data integration service that offers a broader range of functionalities compared to dbt. While dbt specializes in SQL-based data transformations within a data warehouse, ADF provides extensive capabilities for both data movement and transformation across various environments. It supports integrating data from diverse sources, both in the cloud and on-premises. ADF’s integration with Azure services enhances its big data processing capabilities. However, ADF’s GUI-driven approach contrasts with dbt’s code-centric method, making it a better fit for scenarios requiring more complex data integration workflows beyond the scope of in-warehouse transformations.
ADF Quick Comparison to dbt:
- ADF is a cloud-native integration platform, providing the entire spectrum of ETL / ELT
- Documentation tends to be external in ADF, whereas with dbt the documentation is alongside the code
- Data lineage is clear via the GUI but not accessible to non-technical users
- The deployment process in ADF relies on Azure’s deployment and release pipelines instead of relying on Git based CI/CD
Matillion
 Matillion was a very early player in the Cloud ETL / ELT space. It was the first cloud-native ELT platform that I had heard of in the 2010’s (back when SSIS basically ruled my world). It was designed to leverage the power of cloud data warehouses like Snowflake, Redshift, and BigQuery, offering a scalable solution for data extraction, loading, and transformation. It is a comprehensive data integration platform covering dozens of possible sources, targets and transformations.
Matillion was a very early player in the Cloud ETL / ELT space. It was the first cloud-native ELT platform that I had heard of in the 2010’s (back when SSIS basically ruled my world). It was designed to leverage the power of cloud data warehouses like Snowflake, Redshift, and BigQuery, offering a scalable solution for data extraction, loading, and transformation. It is a comprehensive data integration platform covering dozens of possible sources, targets and transformations.
Recently Matillion added support to run dbt and Git directly inside of the platform. Previously they had their own approach to transformation logic, but now I’m seeing a lot of clients use Matillion for integration, then using it to kick off dbt jobs within the platform.
Matillion Quick Comparison to dbt:
- Matillion is a full integration platform, not just a transformation tool
- Follows the ELT design pattern. All transformations are done in-database
- If using Matillions native transformation functionality, the data lineage is not quite as clear as it is with dbt
- Running dbt inside of Matillion will not come with a way to serve the dbt Docs. You’ll need to host the docs elsewhere
- Running dbt inside of Matillion has certain limitations. For example, specifying which environment (target.name variable) you want to run in is currently not possible. This requires cumbersome work-arounds
Alteryx
Alteryx is an interesting anomaly. It is one of my favorite platforms to work in for very rapid transformations, analysis, complex data preparation, etc. They can connect to dozens of sources and write to dozens of targets and accomplish any transformation you can think of. Yet, they do not market themselves as an enterprise ETL solution; rather they are positioned as a business user friendly “data prep” tool and “data science” tool. Alteryx is geared towards rapid insights, and rapid data automation processes, typically combining Excel with database sources, and writing to non-traditional targets like Tableau Server. Their focus on speed and flexibility make it a bit of a pain point for large, control focused IT organizations.
Advantages of Alteryx
- Input data from dozens of sources, output to dozens of destinations
- Intuitive GUI based transformations. They offer dozens if not hundreds of low-code “tools” to wrangle data
- Extremely powerful, flexible, and fun to work with
- Business user friendly, although this is for the business user with the engineer mindset
- Capable of data science, machine learning, and report creation
- Extremely customizable via macros and custom apps
- Can be used as an orchestrator and scheduler
Disadvantages of Alteryx:
- They were very late to the cloud and in fact, still not very cloud friendly
- The S3 input tool feels like an afterthought, leading you to customize Alteryx
- The “Designer” software is desktop native, still no full cloud replacement
- No Git integration or version control (although Alteryx Gallery saves prior versions)
- Because they market towards business users with no data engineering experience, often messy, spaghetti-like workflows are created, leading to technical debt (yes, these suboptimal workflows will become mission critical, with one business person supporting them)
Alteryx Quick Comparison to dbt:
- Alteryx is more than just transformations, it is an end-to-end analytics and data prep platform (and could be considered an integration and orchestration platform)
- Alteryx is Low Code vs dbt is code-first
- No git integration
- Documentation is done via text-box-like objects in the workflow itself
Alternatives to dbt Cloud
DIY: Github Actions
Again I’m going to offer DIY as a legit alternative. But I’m not going to advise against DIY here like I did when discussing DIY transformations.
If all you need is something to run your jobs, GitHub Actions or Gitlab CI jobs has you covered. Or it is fairly trivial these days to use AI host this yourself in the cloud using AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud services. You’ll need a good plan about how you’re going to implement CI/CD, job observability, logging, etc. But, you can do it. I believe in you. Call me if you need help, it’s why I’m here.
dbt Core as a bolt-on offering
There are several companies out there that are leveraging the power of dbt Core within their own proprietary products. There are too many to cover in detail, and in fact I don’t think I can successfully list them all. Here is a list of popular tools which allow you to orchestrate (or run) dbt jobs:
- Fivetran
- Airbyte
- Hevo
- Keboola
- Pure orchestration platforms:
- Orchestra (declarative platform)
- Airflow
- Prefect
- Dagster
- Luigi
- Etc, etc
Orchestra
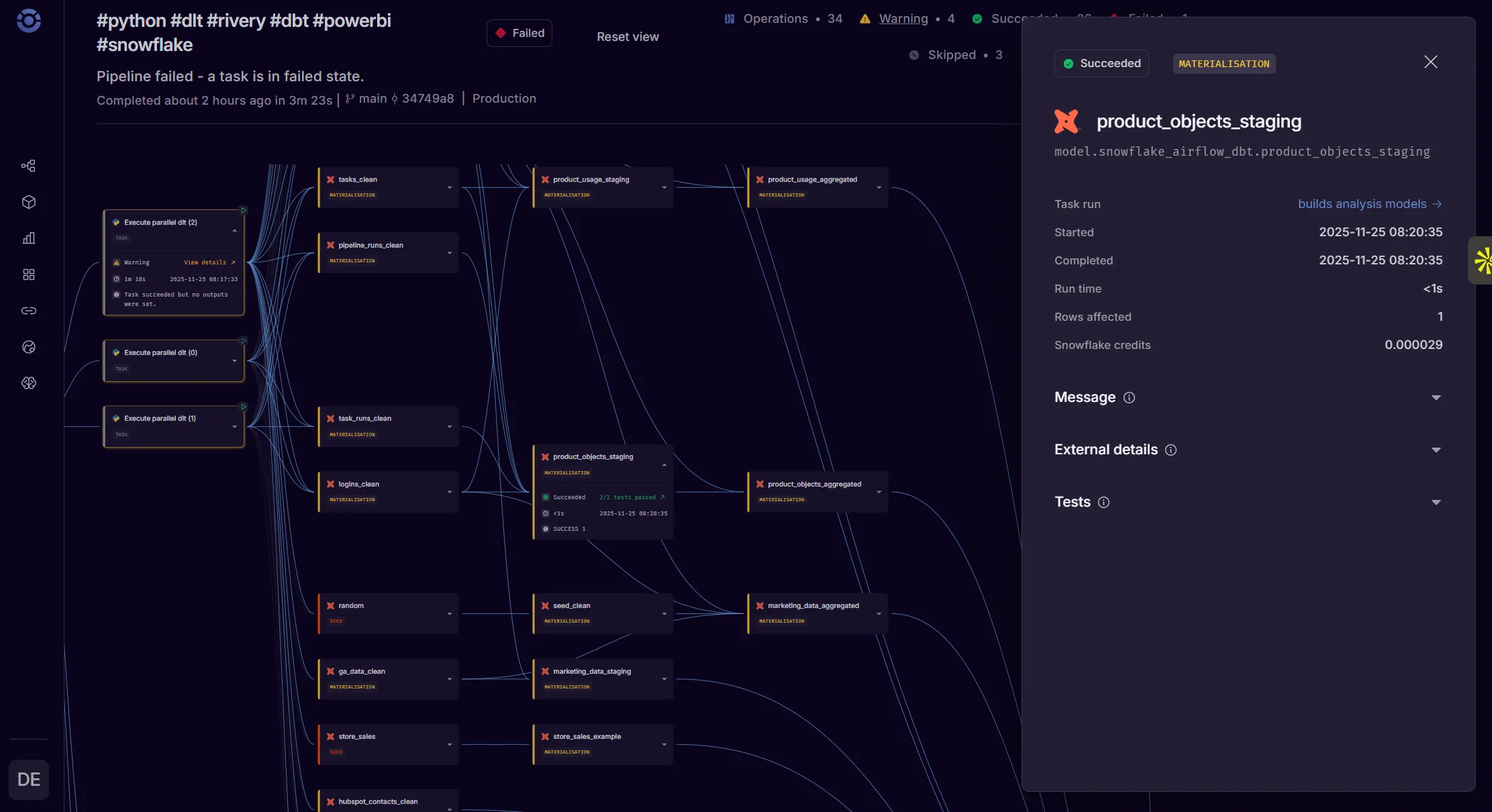
Orchestra is part orchestrator, part compute engine, part visibility tool. Orchestra offers a declarative, .yml based approach to orchestration (wrapped in a slick UI), which means you can get end-to-end orchestration, observability, monitoring, and even metadata management with a config file that’s less than 200 lines of code.
In addition to orchestration, they have first-class support for dbt Core, including managed CI/CD, tons of scheduling options, automatic parsing of artifacts, and even stateful orchestration. The pricing is refreshingly simple: a flat fee of $0.033 per minute. So if you’re running dbt for an hour every day, that’s less than $750 per year.
Orchestra can also run Python and DuckDB as tasks, which opens up a lot of flexibility beyond just dbt jobs. I’ve personally used this to run an Azure Container that runs dlt (data load tool) to extract on-prem data to Snowflake. Orchestra gives you an easy way to insert bespoke and weird pipeline pieces into the puzzle, if you need to.
The service is fully managed, which is brilliant if you’re in the cloud. However, if you’re looking for something you can install locally and run on your own machines, this isn’t for you.
Advantages of Orchestra
- Super fast setup
- Building pipelines is very fast. (use AI to write a config file, or use the UI)
- Version control by default (YAML files in Git)
- Simplified architecture (no need for dbt Cloud, observability tools, DQ tools, etc.)
- Teams get a lot of time back as it’s easy to maintain
- First-class support for dbt Core
- Can run arbitrary Python code or docker containers, so any missing integration you can build yourself
- Fully managed, serverless environments
- 100+ integrations which saves yet more time
- Lineage, catalog, and data quality testing framework built-in
Disadvantages of Orchestra
- Although they have hybrid options, Orchestra is a cloud-deployed control plane
- .yml-based orchestration, so not Python native (like Airflow, Prefect, Dagster, etc.)
- Not all integrations supported out-of-the-box
Try Orchestra
Sign up here or contact the Orchestra team.
Y42
We have saved the best for last!
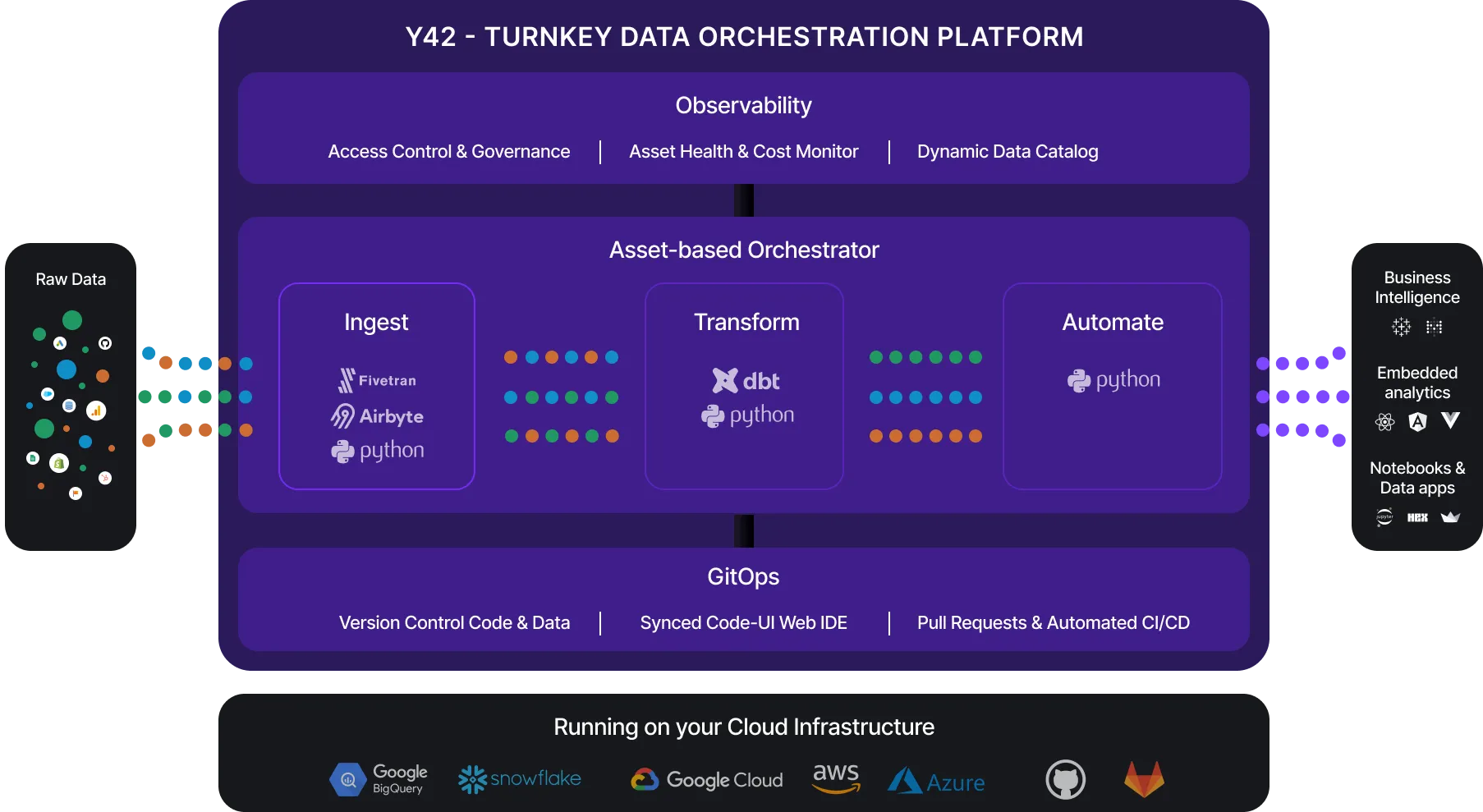
Y42 is a data orchestration platform that packages best in breed data engineering tools under one roof and provides a ton of value-add on top of these tools. Y42 uses Airbyte and cData connectors to ingest data into your warehouse, and hosts a managed instance of dbt Core for you.
Y42 has created a proprietary technology called “Virtual Data Build” (VDB) which allows you to version control your data along with your code. When you roll back to a prior commit, you also roll back the data, automatically.
Advantages of Y42:
- Beautiful, fun to use UI which speeds up the development process
- Best in breed ingest technology (Airbyte, cData) alongside best in breed transformation (dbt)
- Runs Python throughout the platform: custom Python Ingest, orchestrate arbitrary Python Actions (like Airflow), fully featured Python dbt models
- Environment management:
- When you branch
main, you do not need to create a “development environment” in Y42 due to how VDB works. Each branch automatically creates an isolated environment, using zero compute out of the box! - When you merge back onto
main, you don’t need to worry about CI/CD pipelines. Y42 will automatically switch to the latest version of the assets - VDB saves 30% compute cost due to environment abstraction
- When you branch
- Almost all native dbt functionality exists, so it is easy to transition from dbt to Y42
- Column level lineage is available when you move beyond the $0 per month plan
- Due to the GUI nature and fully managed dbt, this could be the easiest way to get started using dbt
- cData brings a lot of Enterprise connectors including NetSuite, SAP, Oracle SCM, Workday, to name just a few. These are coming to Y42 soon
- Option to use GUI or Code to define documentation, tests, and asset metadata
- The orchestration pipelines (job schedules, etc.) are also version controlled
- Robust Asset Health monitoring. At a glance view of status of each data asset
- Version control code and data together
- Automatically roll back data when dbt test fails!
Disadvantages of Y42
- In order for VDB to work, Y42 has replaced
dbtcommands withy42commands. Instead ofdbt bulid, you would runy42 build. This would not be a disadvantage, except they have removed a few native dbt commands - It does not have the Semantic Layer that comes with dbt Cloud
- Updates to dbt Core will not be available immediately in Y42
Contact Y42
https://www.y42.com/book-a-call/discovery
Datacoves
Datacoves is a company that solves the problem of hosting the open source data stack software. They manage a full data stack for you, including Airbyte, dbt, Airflow, and VS Code. Because they are hosting dbt on your behalf, and you can easily schedule DAGs with their hosted Airflow, Datacoves can be considered a valid alternative to dbt Cloud.
Datacoves is a very enticing alternative for those who are looking for the conventional tools in the Modern Data Stack, but don’t want to go through the trouble of hosting each tool.
Advantages of Datacoves:
- Uses native / out of the box dbt
- Hosted VS Code plays nice with dbt and Airflow. It provides a cloud IDE to work with your open source dbt
- Bundling dbt with with Airflow & Airbyte can be very powerful
Disadvantages:
- It may be cheaper to host everything yourself, but certainly not easier
- When compared to dbt Cloud, Datacoves would not have dbt Explorer or dbt’s semantic layer
Wrap Up
The Modern Data Stack is made up of thousands of tools and it is impossible to touch on all dbt alternatives in a single article, but we covered the most popular alternatives here. Remember, when looking for a dbt alternative, it is important to understand if you are looking for something to just replace the Transformation step in ELT, or if you are looking for a full ELT suite. Your motives and business needs are unique, and there is no one-size-fits-all answer. If you’d like bespoke advice, please reach out to me!

About the Author
Jeff is a Data and Analytics Consultant with nearly 20 years experience in automating insights and using data to control business processes. From a technology standpoint, he specializes in Snowflake + dbt + Tableau. From a business topic standpoint, he has experience in Public Utility, Clinical Trials, Publishing, CPG, and Manufacturing. Jeff has unique industry experience in Supply Chain Planning, Demand Planning, S&OP. Hit the chat button to start a conversation!

